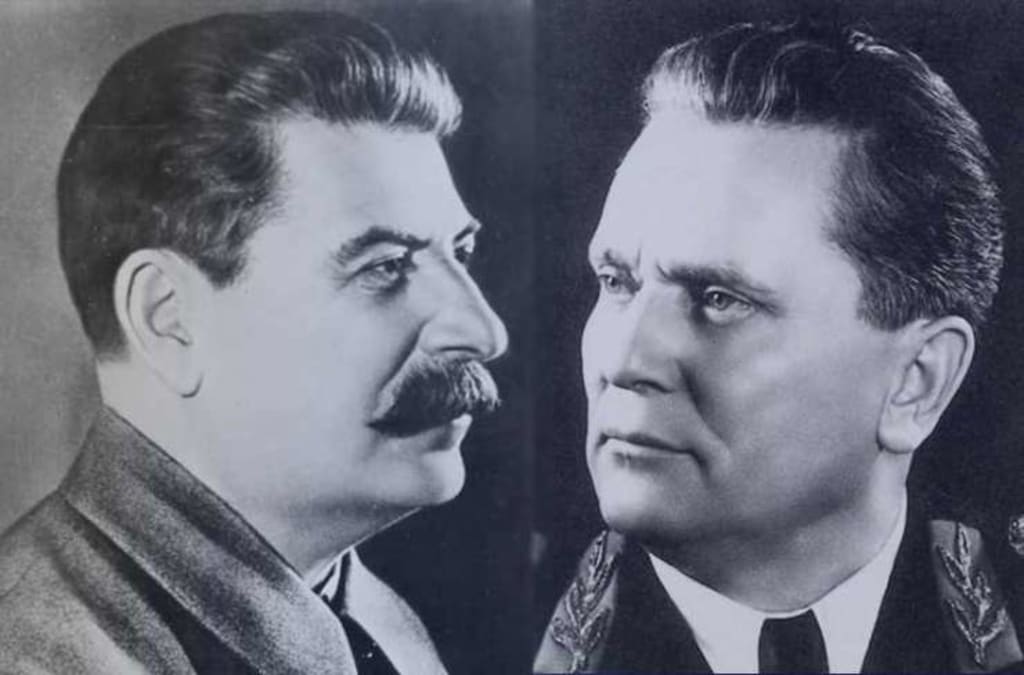
The Yugoslav-Soviet split - Stalin against Tito
During Joseph Stalin’s long rule there weren’t many who managed not only to say no but to openly defy him, especially in the communist realm. Among those few who managed to stand their ground against “the man of steel” were Josip Broz Tito and Yugoslavia. For most of the world, the abrupt end of the Yugoslav-Soviet friendship was a shocking turn of events. Yet the question arises - was the event as important as some have claimed?